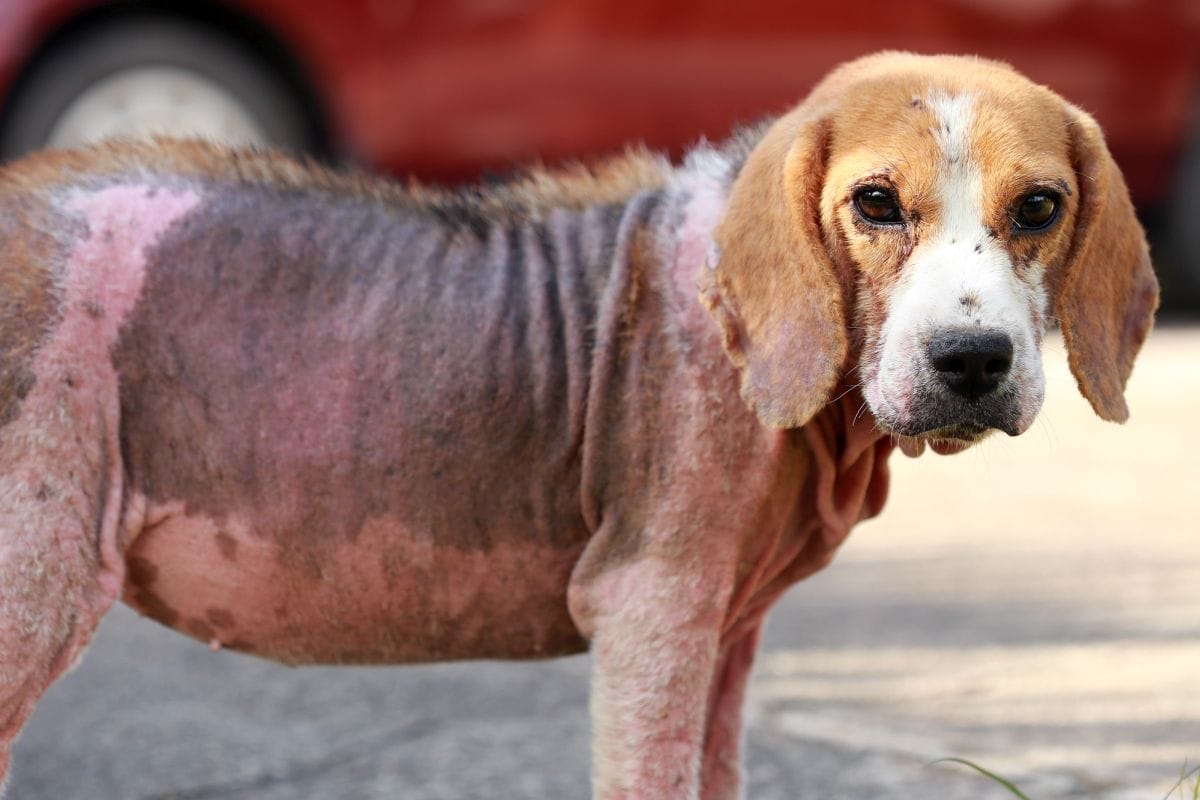
Ringworm, mange, and hair loss in dogs are some of the most common medical issues pet owners face.
They can cause discomfort and distress for your pup, and can be difficult to diagnose and treat.
In this blog post, we will discuss the causes and symptoms of Ringworm Dog Hair Loss Mange and provide tips on how to keep your furry friend healthy and happy.
What is Ringworm?
Ringworm is a common skin infection caused by a fungus, not a worm. It can affect both humans and animals, such as dogs. It is characterized by itching, red, circular patches of skin, and hair loss, and is highly contagious.
It can be spread through direct contact with an infected animal or person, or through contact with contaminated objects.
In dogs, ringworm can cause hair loss and skin irritation, which can lead to secondary infections such as mange.
Hair loss is one of the most common symptoms of ringworm in dogs, and it can be very distressing for owners to see their pets losing hair.
Secondary infections, such as mange, can cause further complications. Mange is a skin condition caused by mites and can lead to intense itching, hair loss, and scaly skin.
Proper diagnosis and treatment of ringworm are essential to prevent its spread and minimize the risk of serious health complications.
A veterinarian should be consulted if ringworm is suspected in a pet. Treatment can include topical medication, oral medication, and environmental sanitation.
It is important to follow the veterinarian’s instructions exactly to ensure that the infection is properly treated and does not spread to other animals or people.
How is Ringworm Transmitted?
Ringworm is a highly contagious fungal skin infection that can spread from person to person, as well as from animal to person and vice versa.
In dogs, ringworm is contracted through contact with other infected animals, as well as through contaminated objects, such as bedding, grooming tools, or clothing.
It can also be spread through contact with infected soil or surfaces, or through sharing grooming items like brushes, combs, or towels. Even contact with infected human skin can cause ringworm in dogs.
When a dog is infected with ringworm, it can cause hair loss, itchiness, and skin lesions. The hair loss can range from small patches to large areas of baldness, and the skin lesions can range from small, circular spots to large, scaly patches.
In cases of severe infection, a dog may also experience mange, which is a skin condition caused by mites that can lead to severe hair loss, itching, and skin irritation.
It is important to diagnose and treat ringworm in dogs as soon as possible, as it can spread to other animals and humans, and can cause serious skin irritation and infection in both.
Veterinarians can diagnose ringworm through a skin scraping or a fungal culture, and treatment typically involves antifungal medications, or in some cases, topical medications. In order to prevent the spread of ringworm, it is important to maintain good hygiene and avoid contact with infected animals or objects.
What Does Ringworm In Dogs Look Like?
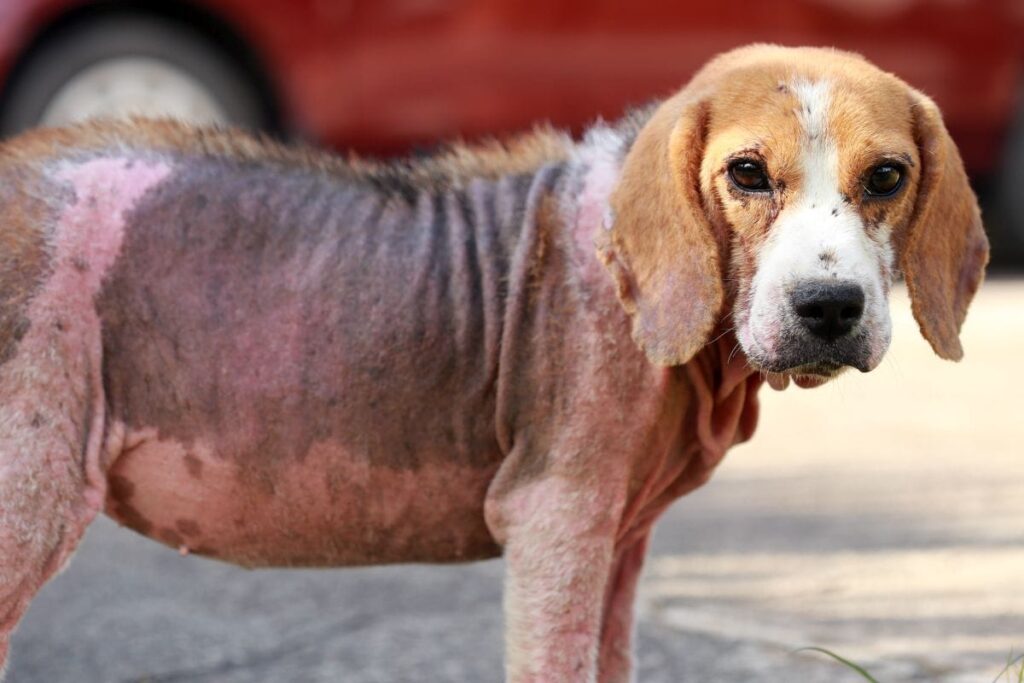
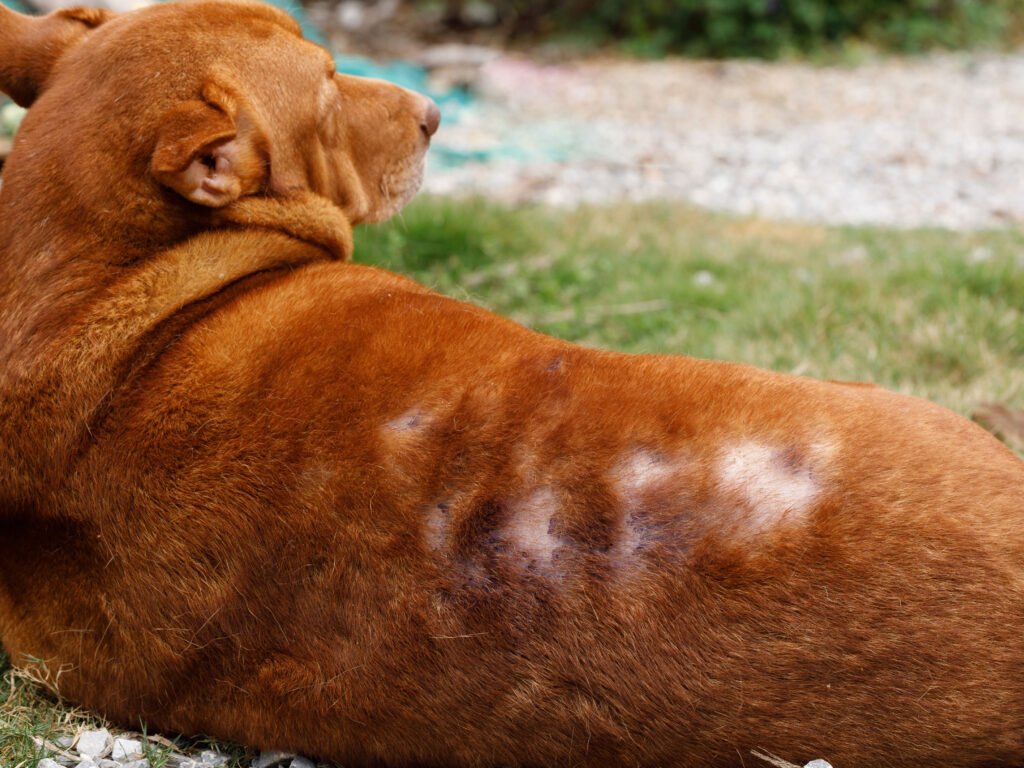
Ringworm is a common fungal infection that can affect dogs, and it often presents itself as a circular patch of hair loss on the skin with raised, reddish-brown margins.
However, not all skin lesions caused by ringworm are round, as the condition can cause patchy hair loss on parts of the body. The hair loss associated with ringworm often appears as thinning or bald patches and the skin may be red and scaly.
In some cases, ringworm can cause inflammation and itchiness around the affected area, and the area may also appear to be greasy and may have a musty odor. In severe cases, ringworm can spread to the claws and cause them to thicken, discolor, and become brittle.
If a dog is suffering from ringworm, hair loss can be seen on its chest, legs, and face. It is important to note that diagnosis and treatment of ringworm in dogs should be done by a veterinarian, as the condition is highly contagious and can be spread to humans.
Treatment for ringworm in dogs includes antifungal medications, topical treatments, and environmental disinfection.
How is a Ringworm Infection Diagnosed?
The most common symptom of ringworm infection in dogs is patches of hair loss, usually accompanied by scaly, reddened skin. Other signs of ringworm in dogs include itching and skin lesions.
The diagnosis of ringworm can be tricky since the signs and symptoms of the infection are similar to those of other skin diseases. A visual inspection of the affected skin is often the first step in diagnosing a ringworm infection.
Your vet may also use a wood lamp, a special handheld light, to see if the affected skin glows, which is a sign of a fungal infection. Additionally, your vet may take a scraping of the affected skin and examine it under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis. A blood test may also be used to detect antibodies to the fungus that causes ringworm.
How is Ringworm In Dogs Treated?
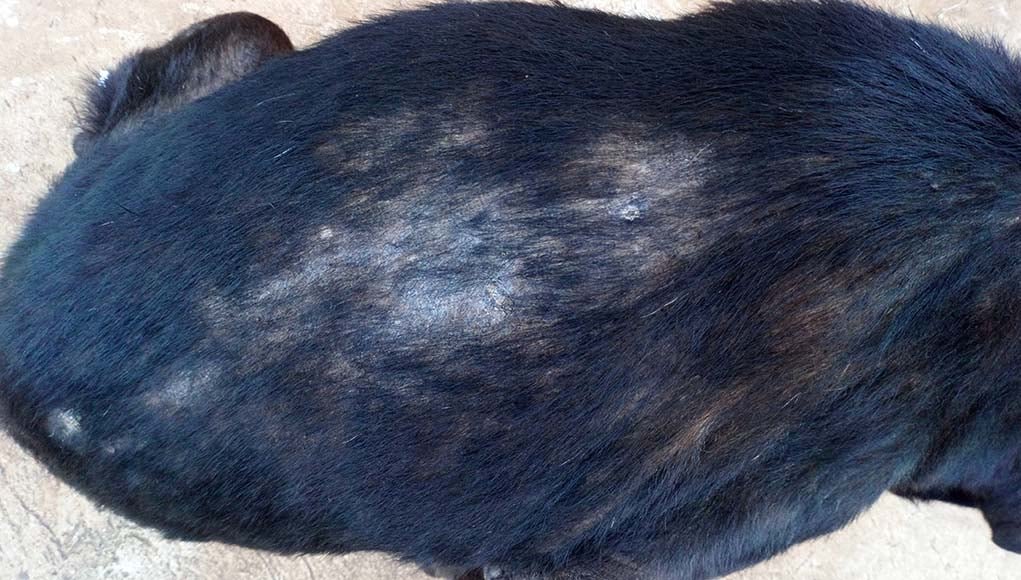
Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the infection but may include topical and oral medications, as well as antibiotics in some cases.
Topical antifungal medications are often prescribed to treat ringworm in dogs. These can come in the form of creams and shampoos, and work by reducing the fungus on the skin and fur.
In more severe cases, veterinarians may also prescribe oral antifungal medications. Additionally, cleaning the affected areas of the dog’s skin and fur can help reduce the spread of the infection and allow for the topical medications to be more effective.
In some cases, it may be necessary to shave the area and treat it with topical or oral medications.
In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat secondary bacterial infections in the skin, which can occur in severe cases of ringworm.
To prevent the spread of the infection to other pets or humans, it’s important to practice good hygiene when handling the dog and to keep the area clean. By following these measures, pet owners can help reduce the risk of ringworm and ensure their dog’s health and comfort.
What is the Risk to Humans?
Humans can contract the disease from their pets, so it is important to practice good hygiene and avoid contact with the infected animal’s skin or fur.
Ringworm can infect any area of the body, including the scalp, face, and feet. In humans, symptoms can include a red, itchy rash, circular patches of baldness, and blisters.
Treatment for Ringworm in humans typically involves topical antifungal medications and, in severe cases, oral antifungal medications.
To prevent the spread of Ringworm, always practice good hygiene and avoid contact with the infected animal’s skin or fur. It is also important to clean and disinfect any objects that may have come into contact with the infected animal.
Additionally, it is important to regularly groom and bathe your pet to remove any fungus that may be present.
If you suspect your pet has Ringworm, it is important to seek veterinary care right away. Your veterinarian can diagnose the condition and provide treatment to help your pet recover. With proper care and treatment, Ringworm can be easily managed and prevented from spreading to other animals and humans.
Conclusion
Hair loss in dogs can be a sign of a number of skin conditions, including ringworm and mange. Both of these conditions are caused by parasites and can be very uncomfortable for your pet. The key to treating both conditions is to identify the underlying cause and seek treatment from a veterinarian.
In many cases, ringworm can be treated with topical antifungal medications, whereas mange requires systemic medication. Depending on the severity of the condition, your veterinarian may also recommend additional treatments such as shampoos, medicated baths, and creams.
Prevention is key when it comes to both conditions, and good hygiene and regular veterinary check-ups are recommended.
If your pet is exposed to ringworm or mange, it is important to keep your pet isolated from other pets and to clean your pet’s bedding and living space regularly. Regular grooming and flea control can also reduce the risk of both conditions.
It is important to note that hair loss due to ringworm and mange can take some time to resolve, so it is important to be patient and follow your veterinarian’s instructions. If you have any questions or concerns about your pet’s condition, be sure to speak with your vet.